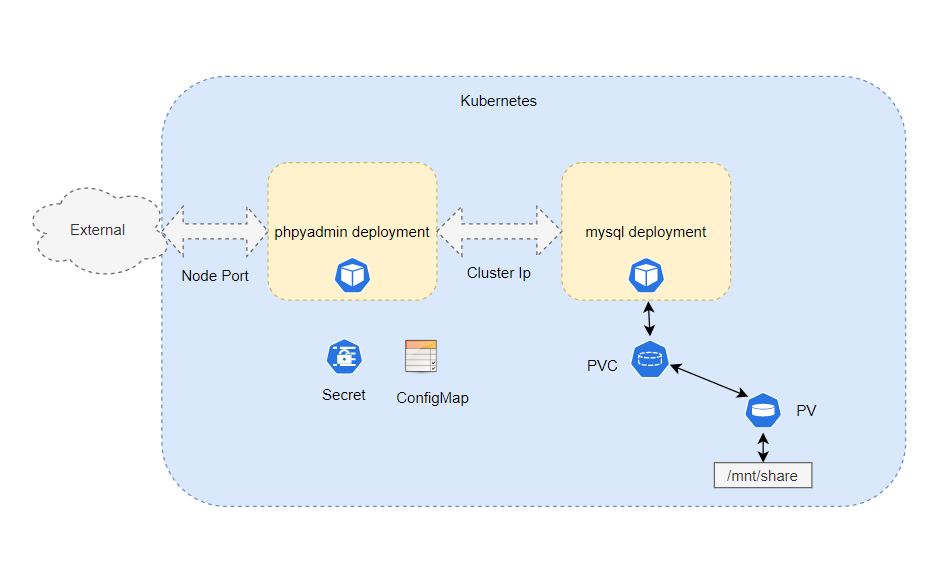
Here, I am covering concepts of persistent volume (PV) & persistent volume claim (PVC). In the previous blog I have covered how to deploy PHPMyAdmin application in kubernetes. PHPMyAdmin application does not have a persistent storage. Hence If MySQL pod die due to some unexpected error for e.g. resource crunch then data stored in database will also get deleted as data by default stored in pod. Pods by default are stateless in nature. Hence to persist MySQL data PV & PVC is required.
Persistent Volume (PV)
Storage provisioned by administrator. Learn more here
Persistent Volume Clain (PVC)
Request for a storage by user. Learn more here
Architecture
Prerequisites
Deploy
PHPMyAdminApplication Follow Deploy phpMyAdmin application on kubernetes blog.Go to
session_2directorycd ../session_2/
Step 1: Create NFS share
Reference:
- https://www.linuxbabe.com/ubuntu/nfs-share
- https://vitux.com/install-nfs-server-and-client-on-ubuntu/
I have created NFS mount at /mnt/share location on VM with IP 192.168.1.6
Step 2: Create Persistent Volume (PV)
kubectl create -f db-pv.yaml
Step 3: Create Persistent Volume Claim (PVC)
kubectl create -f db-pvc.yaml
Step 4: List PV & PVC
kubectl get pvc
kubectl get pv
Step 5: Redeploy MySQL deployment
kubectl delete deployment db
kubectl create -f db-deployment.yaml
Here db-deployment.yaml is updated YAML with volume & volume mounts. Next watch pods.
kubectl get pods -n watch
Exit once db pod goes into running state.
Step 6: Go to mount directory and list files
cd /mnt/share
ls -ltr
Step 7: Browse PHPMyAdmin application and create database
Step 8: Delete pod
kubectl delete pod <MYSQL_DB_POD_NAME>
Step 9: Browse PHPMyAdmin application and verify database still exist