Introduction
Pointers is Go is one of the most complex concepts especially for beginners. In this blog, I have explained the Pointers in a very simple format through visualization and point-by-point explanation. Please read the full blog for complete understanding. To start with let me give you the definition of Pointers:
Pointer stores the memory address of the variable instead of the value of a variable.
This makes it different from other types of variables.
Pass By Value
Let me explain to you the concept of Pass By Value before going deep in understanding Pointers. If you understand this then It will help you in understanding the code with extensive use of Pointers. In Pass By Value the value of a variable is copied into the calling method argument instead of the reference or memory address of the variable. Just remember this simple formula:
Go always follows Pass By Value and not Pass By Reference
Let’s see How Pass By Value works in Go.

Refer to source code here.
- Variable
xof type string is defined and the value “Sagar” is assigned to it. - Method
addSurname()is called withx, Here the value ofxthat is “Sagar” is copied to variabley - String “Jadhav” is appended to the value of
yand the result is assigned back toy.
So updating the value of y doesn’t update the value of x as both are different variables but storing the same value.
Pointer in Action
In the above example How to change the value of x by updating the value of y? Here Pointers come into the action. Yes, It is possible to update the value of one variable through other variables with the help of Pointers. Let me explain you through the below example:
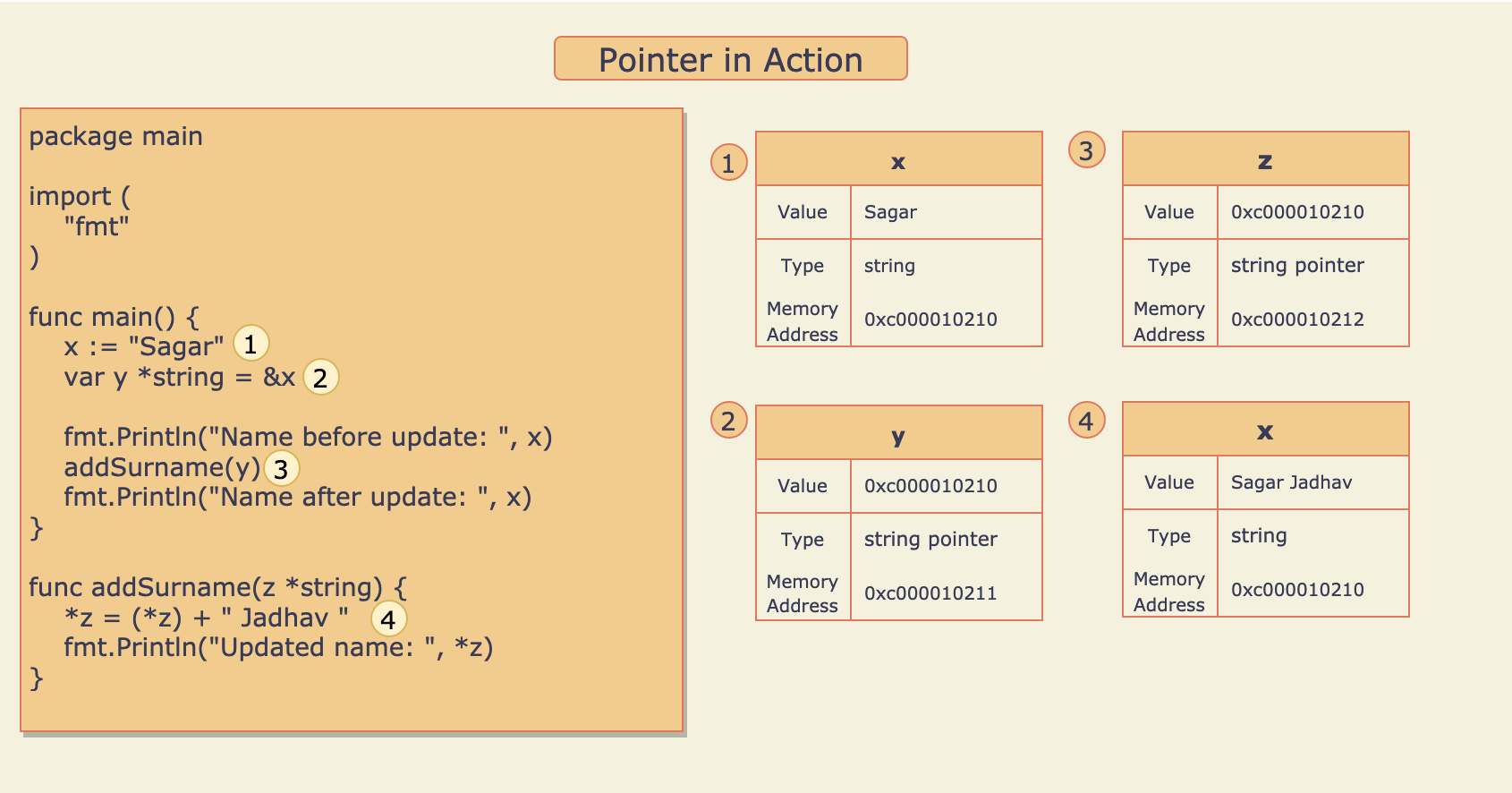
Refer to source code here.
- Variable
xof type string is defined and the value “Sagar” is assigned to it. - Variable
yof type string pointer is defined and the address ofxis assigned to it. - Method
addSurname()is called withy, Here the value ofythat is the address ofxis copied to variablez. - String “Jadhav” is appended to the value at address stored in
zand the result “Sagar Jadhav” is assigned back to the variable at the address stored inz. Sounds complicated, Map this point with the above picture for better understanding.
Pointer Receiver
The use of Pointer with Structs is very common, Hence understanding this concept is a must. Let’s get deep-dive through the below example:
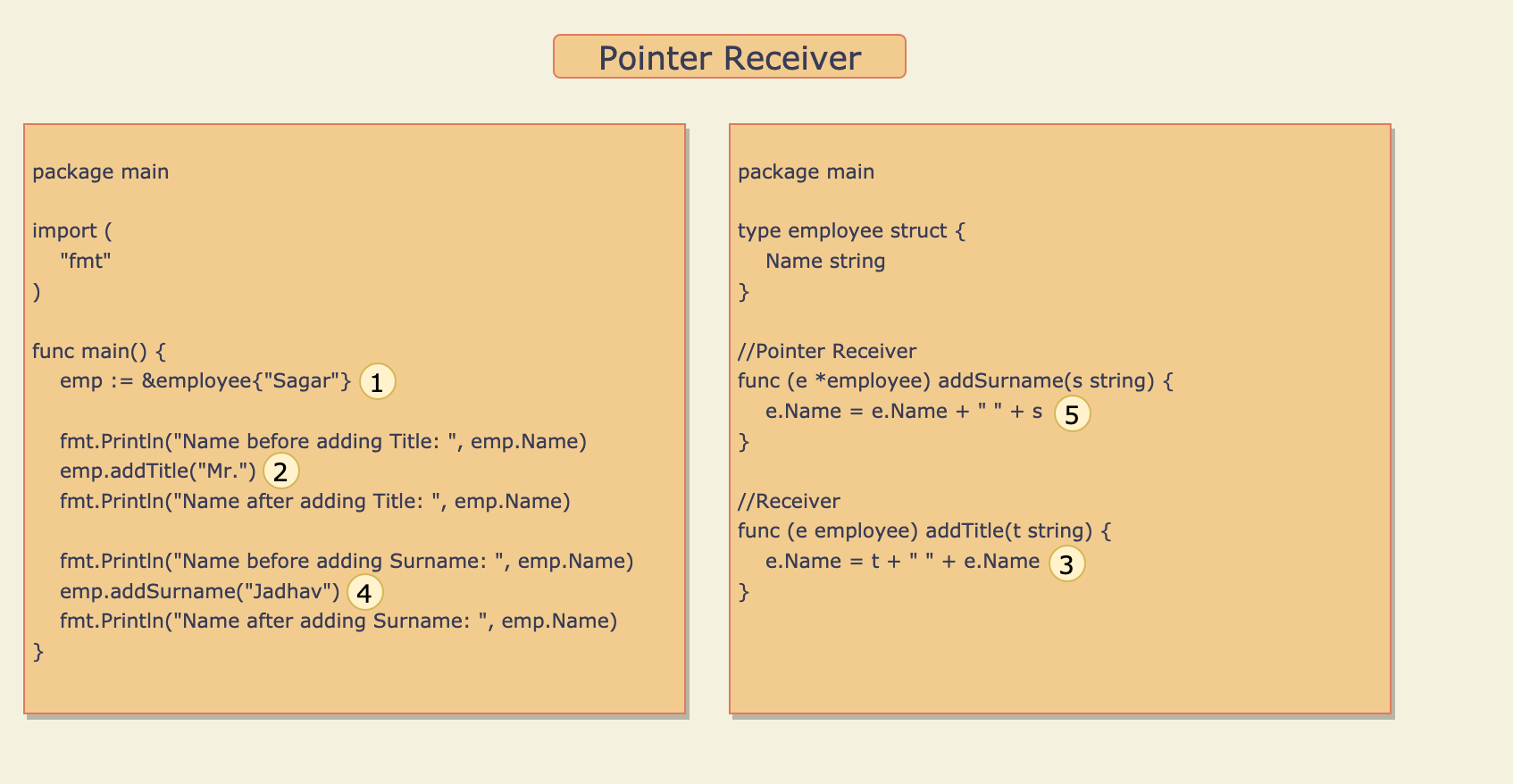
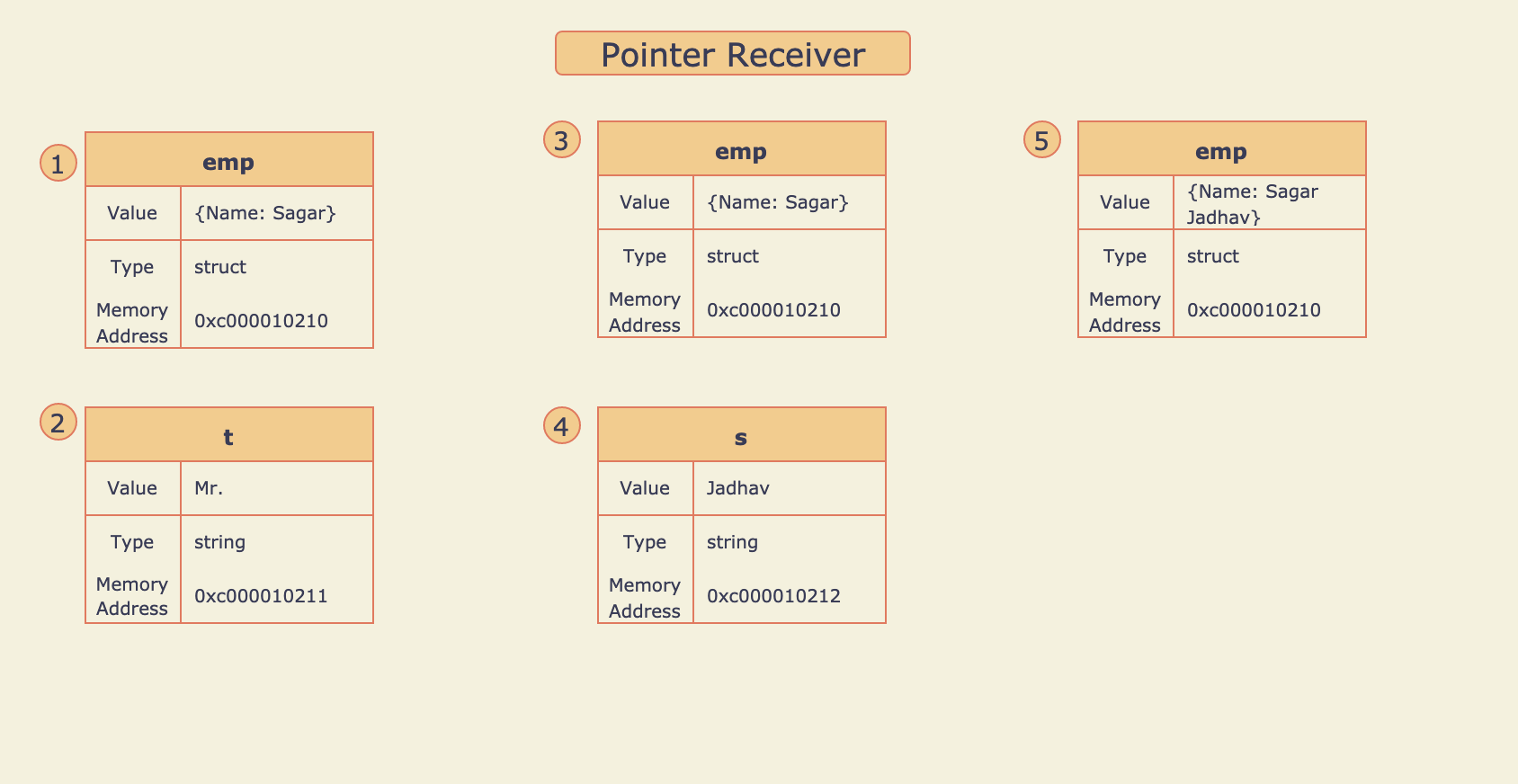
Refer to source code here.
- Variable
empof type employee struct is defined and the propertyNameis initialized with value “Sagar”. - Method Receiver
addTitle()is called with string “Mr.”, Here the string “Mr.” is copied to variablet. - Value of
Nameproperty is appended to Value oftand the result “Mr. Sagar” is assigned back to theNameproperty. But here theNameproperty ofempis not updated becauseaddTitle()is a method receiver so when it is called, Value ofempvariable is copied to another variablee. So any updateewill not affectemp. - Pointer receiver
addSurname()is called with string “Jadhav”, Here the string “Jadhav” is copied to variables. - Value of
sis appended to the value ofNameproperty and the result “Sagar Jadhav” assigned back to theNameproperty. Hereempvariable is updated because variableeis a pointer toempso any changes inewill also affectemp.
Checkout here for more details.