Intend of blog is to explain use of following kubernetes resources using phpMyAdmin application deployment:
- Deployment
- Service
- Secret
- ConfigMap
Before going deep dive into deployment architecture let’s first understand this concepts.
Deployment
Deployments represent a set of multiple, identical Pods with no unique identities. Learn more here
Service
Services are use to group pods together using labels & selectors. Learn more here
Secret
Secrets are used to store confidential attributes such as password, API key etc. Learn more here
ConfigMap
ConfigMaps are used to store configuration parameters such hostname, port etc. Learn more here
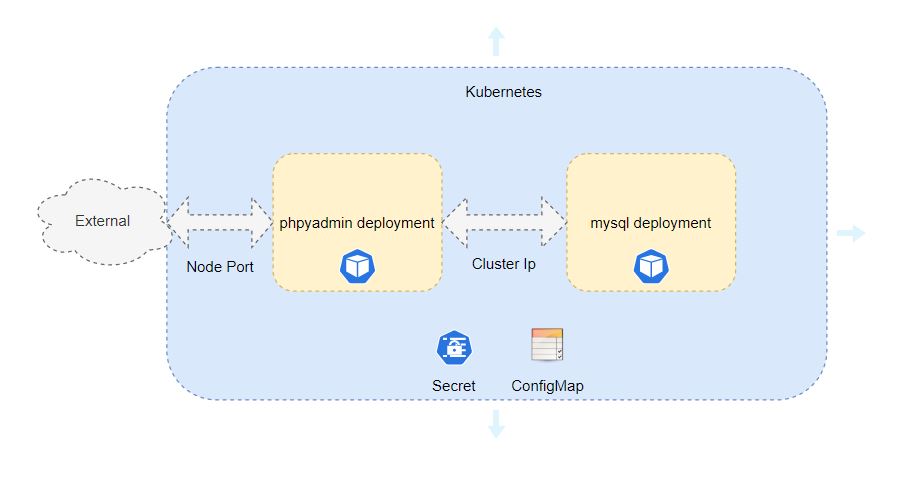
Architecture
phpMyAdmin application comprises of two components UI (phpMyAdmin) and database (MySQL).
Prerequisites
Clone github repository
git clone https://github.com/sagar-jadhav/kubernetes-essentials.gitGo to
session_1directorycd ./kubernetes-essentials/session_1/
Step 1: Create demo namespace
kubectl create namespace demo
Step 2: Set current namespace to demo
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=demo
Step 3: Create secret db-secret
Store MySQL root password in secret.
kubectl create -f secret.yaml
Step 4: Create configmap db-config
Store host & port in configmap
kubectl create -f configmap.yaml
Step 5: Create deployment for MySQL
kubectl create -f db-deployment.yaml
kubectl get pods --watch
Exit when pod goes into running state
Step 6: Create service for MySQL
Here service type ClusterIP is used so that it is accessible only inside the cluster.
kubectl create -f db-service.yaml
Step 7: Create deployment for phpmyadmin
kubectl create -f phpmyadmin-deployment.yaml
kubectl get pods --watch
Exit when pod goes into running state
Step 8: Create service for phpmyadmin
Here service type NodePort is used so that it is accessible outside the cluster.
kubectl create -f phpmyadmin-service.yaml
Step 9: Browse phpmyadmin application
Go to browser and browse http://IP_ADDRESS:30030. Login with root user & test password. Here IP_ADDRESS is the ip address of virtual machine where kubernetes is running.